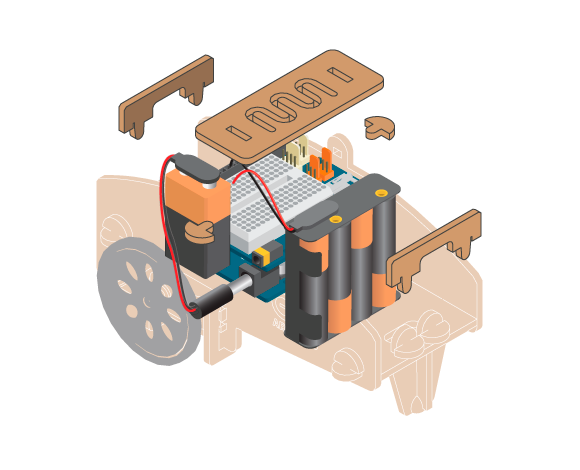
The Line Follower does exactly what the name suggests, it follows a line. Make it go where ever you want by showing the way with a 3 cm wide, black line.
Materials
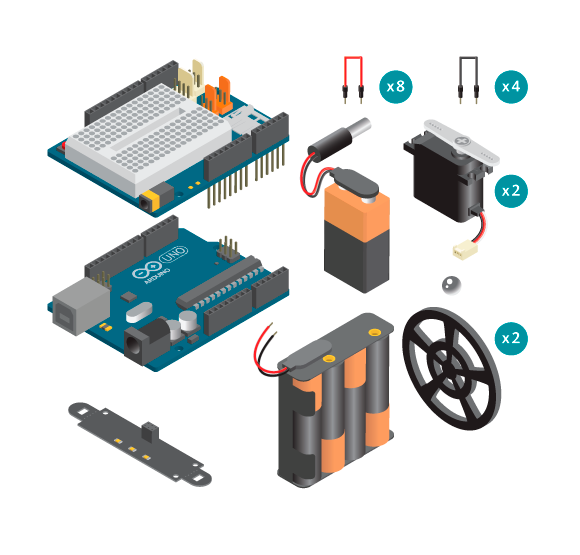

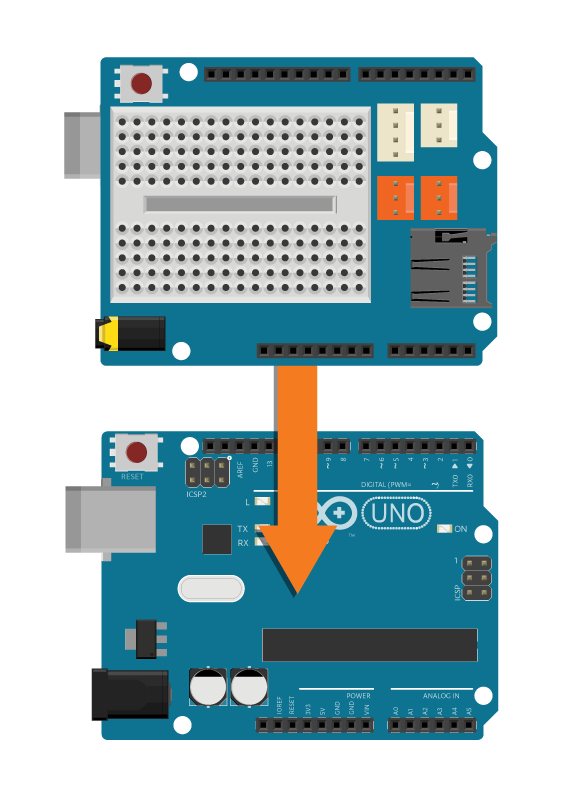
- 1 Arduino Uno board
- 1 Education Shield
- 1 IR Array
- 2 continuous rotation servos
- 4 black jumper wires
- 8 colored jumper wires
- 1 9V battery
- 4 AA batteries
- 1 AA battery holder
- 2 power plugs (One without the plug but with two loose wires)
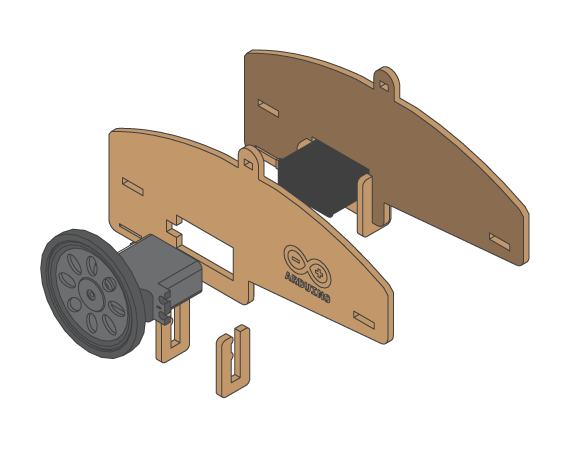
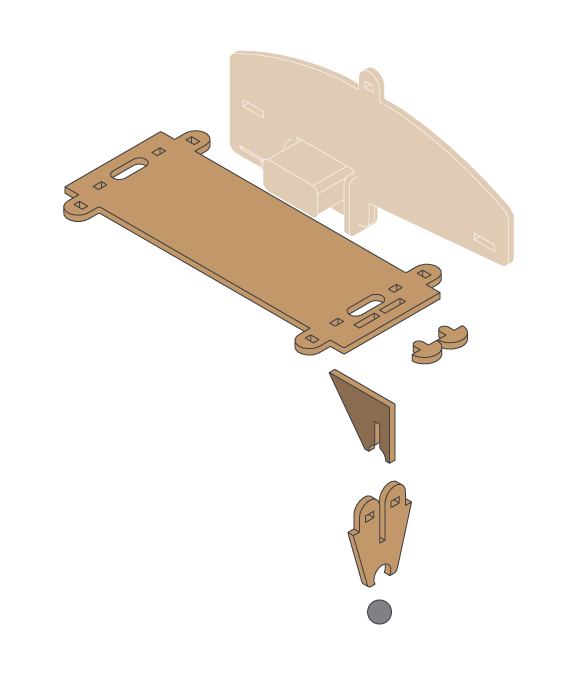
- Line follower kit
- 1 metal ball
Instructions
Code
Find the code in File>Examples>EducationShield>Block4-Robots>Projects>LineFollower
How it works
- The EducationShield and Servo libraries are included.
- The IRArray and Wheel objects are declared,
irandwheel. - In
setup()the wheels are initialized. - The program pauses for 1000 milliseconds.
- In
loop(), the variablediris declared to hold the value read from the IR array usingreadLine(). The value will be between -100 and 100 and represents the direction the black line is heading. wheelsis set to follow the value ofdir.loop()continues to loop.
Troubleshooting
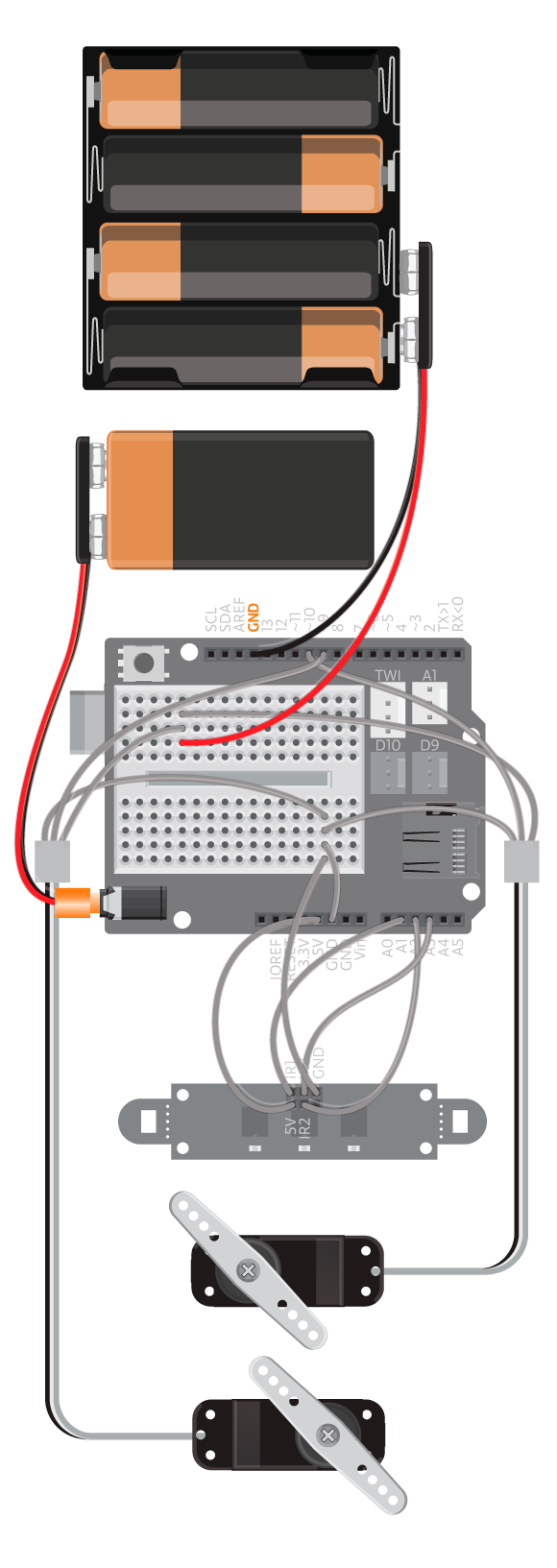
- Refer to the illustration and double check your connections. Make sure the shield and jumper wires are firmly connected.
- If the motors are not working, see the reference about how to debug servo motors used as wheels.
- Debug the IRArray, see the IR Array reference.
Experiment further
- Print a track and build obstacles for the robot. If the obstacles are too difficult, see if there is a way to improve the robots performance by modifying the wheels.
- Make the robot react in some way when it “sees” only white. That is, when it has lost the track of the black line.